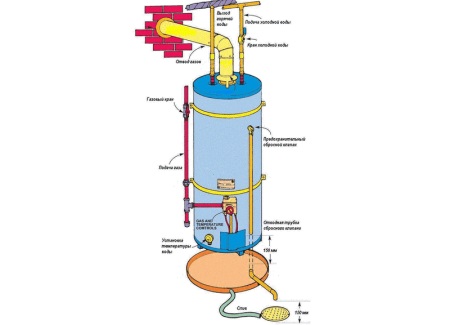
Structure and operation of the boiler

Solving the problem of hot water in a country house or private home or in a city apartment, very often stop at the purchase of a boiler. To choose a suitable version of such equipment, it is necessary to understand how the boiler is arranged and on what principle it functions.

What is a boiler?
This is the name of a type of storage water heater. The boiler heats water continuously to supply the apartment or private house. For heating such a device can use gas, electricity or other types of fuel.

The device depending on the type
Direct heating
The energy carrier, which goes into such devices, is spent only on heating water inside the device. This means that devices of this type themselves produce heat, which heats the water. They can be gas, when a gas burner is used for heating, as well as electric, that is, with heating by a heating element.

By design such boilers are a capacity (tank with water), around which there is thermal insulation and an outer casing with a control panel. In addition to the heating element (burner or TEN) in such devices are present magnesium anode, a thermostat, a group of security and spigots (input and output).
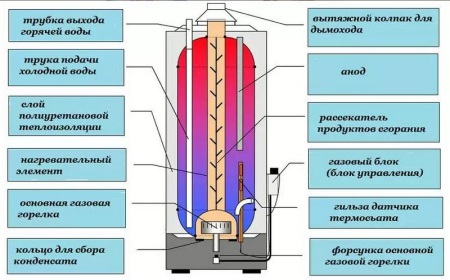
Indirect heating
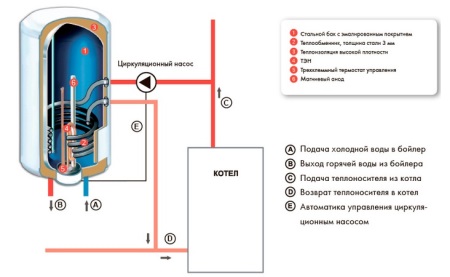
This type of boilers are installed in houses or apartments with autonomous water heating, providing the presence of a single-circuit boiler. Water temperature inside the boiler with indirect heating increases not due to the direct impact of the energy source, but as a result of heat exchange with the heating circuit.

The design of this type of boiler includes a casing, inside which there is an inner tank, separated from the outer casing by a layer of thermal insulation. Water from the cold water supply pipes enters the tank through the incoming pipe, and is removed after the opening of the tap of hot water through a pipe located in the upper part of the device.
Separately in the unit there is a heat exchanger, which in most models is represented by a coil. It can be evenly arranged inside the tank or located at the bottom of it. Both pipes of such a heat exchanger are connected to the heating boiler.
The coolant from the boiler moves through the heat exchanger, heating the water in the tank by heat transfer, and then output through a separate pipe, returning to the boiler. Such a heat exchanger is most often one, but there are models with several heat exchangers that can be connected not only to the gas boiler, but also to another source.
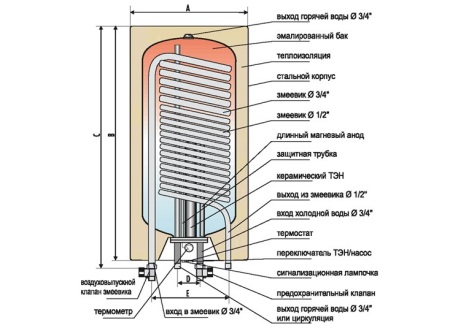
There are also indirect heating boilers without coils, the design of which is called a "tank in a tank" due to the presence of another tank inside the tank of such a boiler. Sanitary water in such a device is heated in the inner tank, and the coolant moves between the walls of the inner tank and the outer walls.
Some models of boilers of this type may have a recirculation pipe. Mandatory elements of all such devices are a magnesium anode and a safety group, as well as the temperature sensor. In large boilers with a capacity of over 150 liters is often provided with a revision window.
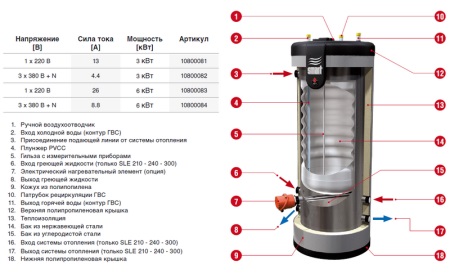
Combination
Such boilers combine the two previous types of heating devices. By design, they are represented by devices with indirect heating, but differ by the additional installation of a heating element, allowing you to use the device as a storage electric boiler of direct heating. This is especially in demand for the summer period, when the single-circuit boiler is off.
Device according to the type of energy
Electric
Such boilers are the most common and are available in a wide range. For their work, they use electricity, so the main detail of such devices is a heating element. It is this part that heats the water drawn into the tank of the device. TEN can be located directly in the water or be placed in a capsule and not in direct contact with water (such a TEN is called "dry").
Next to the heating element there is a temperature sensor, which controls its operation through an electromechanical or electronic thermostat. These parts ensure that the water inside the tank is kept at the correct temperature. As soon as the water cools down a little, the temperature sensor sends a command through an electrical circuit to the thermostat, as a result of which the heating element begins to heat water.

The tank of the electric boiler is surrounded on the outside by a layer of insulating material, as well as a decorative body of plastic or steel. Cold water enters the unit through a pipe located at the bottom of the boiler. As the liquid heats up the liquid rises to the top of the device, from where it is withdrawn through the outlet pipe after turning on the tap with hot water.
Inside most electric boilers there is a magnesium anode. Because of its lower electrical potential, such anode attracts free ions of those salts that are dissolved in tap water. As a result, limescale is deposited on the anode instead of attacking the heating element and the tank walls. Over time, the anode deteriorates, so when you regularly service the electric boiler, replace it with a new one.
At the inlet of the electric boiler a safety group with a safety valve must be installed. Its presence is important to protect the boiler from excessive pressure. If the pressure inside the tank rises, the valve releases it and thereby prevents damage to the device.
For more information, about boilers of this type, see the following video.
Gas
This type of storage heaters is not as common as electric boilers, because of the complexity of the installation (you need to coordinate, the presence of a flue, good ventilation, registration).
Such heaters run on natural gas. Their design includes a water tank, incoming cold water supply pipe and hot water outlet pipe. The body of the device is thick enough and separated from the water tank by a layer of insulation to maintain the temperature of heated water for a long time.
Heat exchange in gas boilers occurs through the bottom wall of the water tank, because under it there is a combustion chamber with a gas burner located in it. Also, the heat is transferred to the water inside the tank from the central channel through which the combustion products from the combustion chamber to the chimney.
In such a boiler is controlled by a temperature sensor and thermostat. These elements fix the temperature of the water and, if necessary, turn off or on the gas supply to the burner. Also, gas boilers have a safety group, the main part of which is an emergency valve to release excess pressure.
To inside the unit on its walls is not deposited scale, the design of the gas boiler includes a magnesium anode. Over time, it "eats away", so it requires replacement.