All about ventilation in the bath

To know everything about ventilation in the bath is no less relevant than about boilers and walls, about the foundation and drainage. Knowing how to make the hood, and how to properly equip with their own hands other components, people can easily avoid mistakes.
Be sure to understand the schematics, including the device bastu ventilation and other systems in the steam room of the sauna, with other features.

Features
The functions of ventilation in the bath are about the same as in a residential house or other room. We are talking about the exchange of air masses. However, its work is considerably complicated by the fact that we have to supply more air. Particularly many problems arise when using different types of fuel. Combustion is only very efficient if there is plenty of airflow. If the ventilation lines are not efficient enough, you feel uncomfortable - and at high temperatures you might even faint.
But it is important to take into account the peculiarities of the specific type of rooms. In the Russian bath is one environment, but in the Finnish sauna there are very different conditions. And in both cases the difference between separate rooms - steam room, washing room, vestibule - is significant. The Finnish approach implies that the wall constructions must be ventilated - this is achieved by means of counter battens to allow air to pass through. It also requires the use of active extractors (and sometimes active air distribution throughout the room).
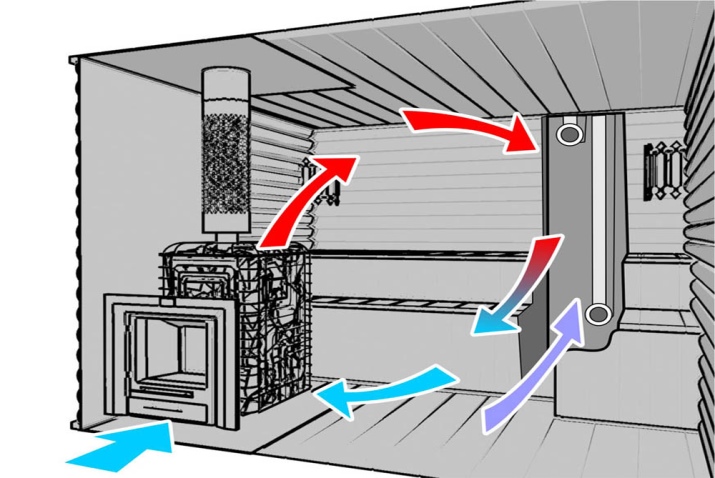
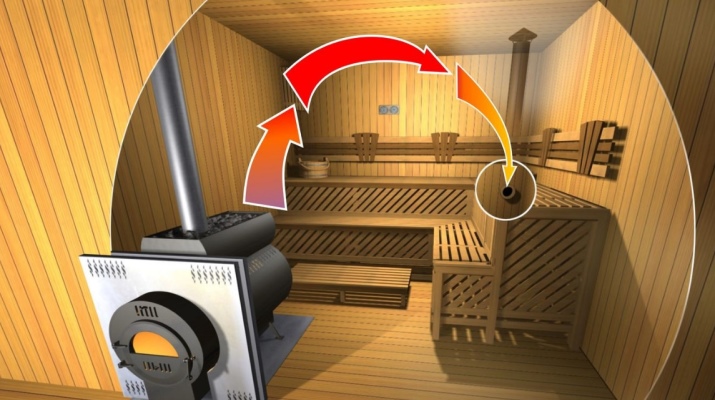
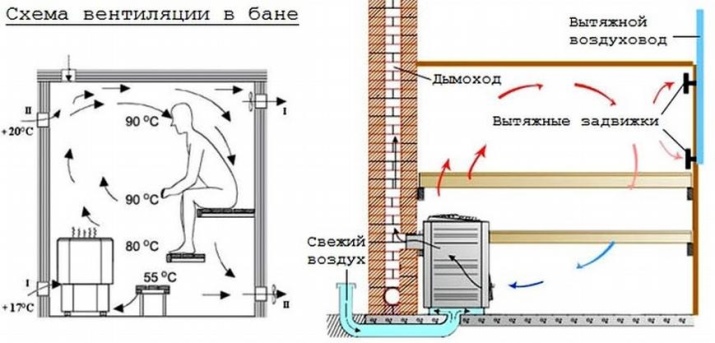
Inside the sauna, the entire air volume should be replaced at least 5 or even 6 times per hour. It is quite reasonable to put complex and powerful hoods in order to maintain the design saturation of steam and moisture precisely. That is why boxes and special fans often become everyday components of saunas. Such active ventilation is not required in a Russian bath.
In many cases, in general, is limited to a single salvo ventilation, that is, ventilation through the open window and door, but such a solution works well for only a small area.


Types
Natural
This system uses natural air circulation. The moment it heats up, it becomes lighter and rises to the ceiling. This property allows you to ventilate baths and saunas sometimes from the steam without any additional devices. Well-calculated openings working - one to throw in fresh and the other to remove the overheated and over-moistened air - are enough. Additional sources of heat other than stoves or conventional hearths are not needed, and there is no need for fans.

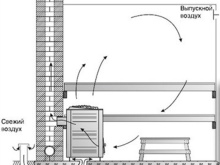

It is only necessary to competently determine what size openings should be for a particular room. A rational arrangement of windows will help to simplify the task. At least one of them should be put in the steam room to improve ventilation. The supply part is usually located near the ash-pit at the level of the floor covering.
This solution will guarantee the intake of fresh air without the use of additional fans; the exhaust part of the ventilation is often installed in front of the wall where the supply is located.


Returning to the windows, it should be pointed out that they do not cancel the need to arrange the openings, but complement them. In the classic Russian sauna, in general, try to equip the steam room with two windows. One is placed over the shelves in front of the door, only to lower the temperature if it is too high, or look outward. You don't need a big window here.

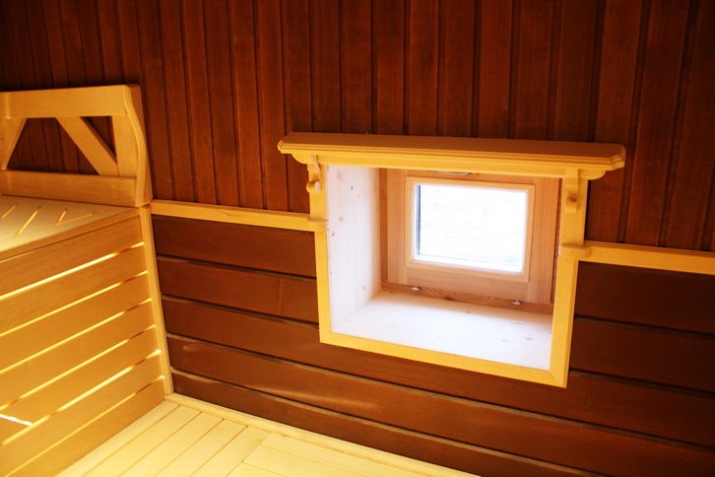
Auxiliary window is placed under the shelves, and it is not even necessary to put high-quality transparent glass; the main task - good ventilation of the most stagnant zone in the whole bath.

Forced
The use of heat-resistant fans for extraction allows you to ensure normal ventilation even in the full calm on the street. By means of special devices a pressure difference is formed in separate parts of the bath. The simplest indicator of such a difference is a change in the slamming of the door. But it is unwise to force the air flows too much. In this case draughts may occur, which are subjectively unpleasant and even directly harmful to health.



Combined
The device of natural ventilation is economical and relatively simple. But sometimes its capabilities are not enough just a little, and a fully forced air exchange will be excessive. In this case it is necessary to use a combined scheme. One of the openings is equipped with a fan, which is chosen as carefully as possible. The other - leave to work in a natural mode, taking into account the peculiarities of a particular project.


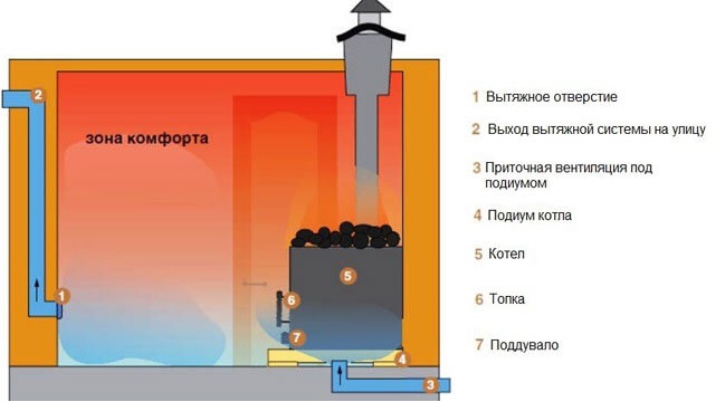
Deserve special attention is the so-called bastu system. Usually it is arranged as follows:
-
The air enters the steam room through a supply line;
-
As it passes below the furnace - in the floor or in the lower part of the wall - the temperature increases;
-
the warm air at the very top of the room immediately mixes with the water vapor;
-
gradually it cools down and moves outside through a special opening;
-
The vertical pipe warms up from the outside, which stimulates the outflow of air masses;
-
Then they enter the horizontal "tee", located inside the room, the end of which closes the plug.
What type to choose, taking into account the material of the walls of the bath?
But the ventilation must also be adapted to the type of construction materials. For example, in a sauna made of foam blocks, air and air intake ducts are very important - no less than in conventional wooden structures. Hygroscopicity strongly affects the basic blocks. Occurrence of condensation should therefore be avoided at all costs. In any case there should be in-wall models.
Such structures involve the formation of a ventilation gap between the hydraulic insulation and the cladding. The air moves actively along it. The gap when forming the external cladding should be 40-50 mm. Inside the room its size is 30-40 mm. Such a gap is achieved with the help of purlins, which holds the decorative wall cladding.
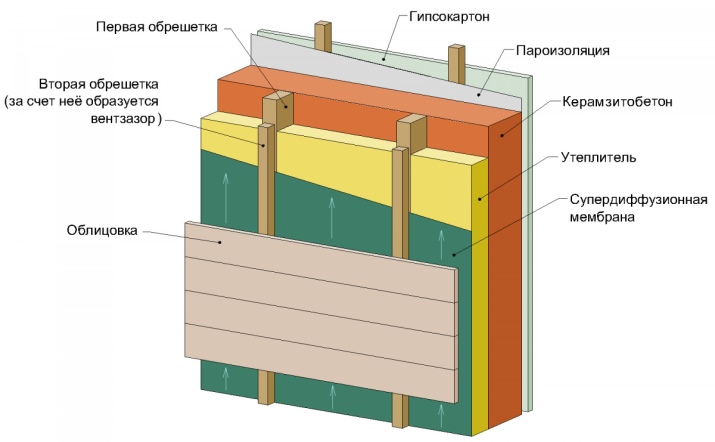
An attempt to use only inside the wall ventilation will turn out that moisture will still appear. Inside ventilation channels allow air renewal and accelerated drying of the material. And therefore the integrity of blocks is greater, and also makes it easier to care for the room. It is recommended to combine the wall and located inside the ventilation system also in the secondary rooms.
In a wooden bath, high quality ventilation is also very important. In the absence or low level of it in a couple of years, the structural materials can decay and fail in a matter of 2-3 years. Even before that, an unpleasant odor appears, which is almost impossible to "block" with any means. There is a danger of carbon monoxide accumulation and formation of mold nests.
In a wooden bath, the ventilation system should be quite powerful; the same system is needed in a frame or made of timber (log) construction.
Ventilation is provided by means of:
-
ventilation valves;
-
vents;
-
slightly open vents.
Boards are placed on the lag so that there were gaps of about 0.5 cm. The absence of stagnant water allows air to flow indefinitely to all parts of the flooring. Allowed lead ventilating pipe from the basement to the riser. It itself is located above the most elevated point of the roof, with a deflector crowned. The outflow of air through the attic is unacceptable, because it will cool the room; similarly, ventilation can be designed and in a brick bath.
If the sauna is made with an electric heater, you still need to ventilate. No matter how much they talk about "dry" air, it's hard to do without normal exchange. The inflow must immediately fall on the heated stove. It will heat itself and take away heat. The size of the gaps under the door is from 3 to 5 cm in a dry sauna total index of exchange should be at least 10 times per 60 minutes.
How to properly equip their own hands?
In the steam room.
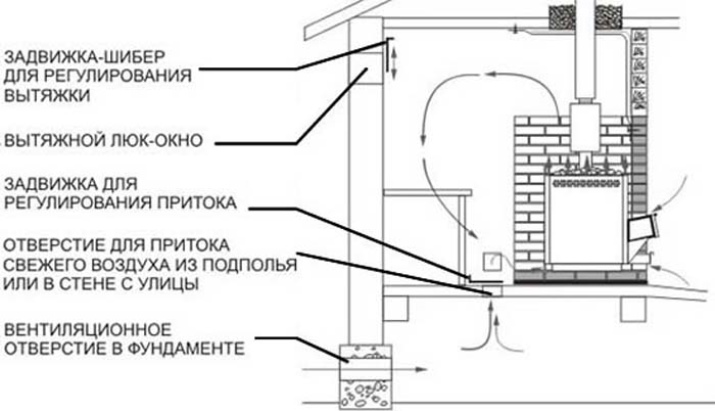
On the wall opposing the intake line from above, form an additional extractor. It will be overlapped for the time of use (while the bath is heated and washed in it). Using it during steam procedures is all the more prohibited. As soon as the session is over, you must immediately open this hole, which improves ventilation and drying. Ventilation of the steam room through the foundation can be arranged quite well.
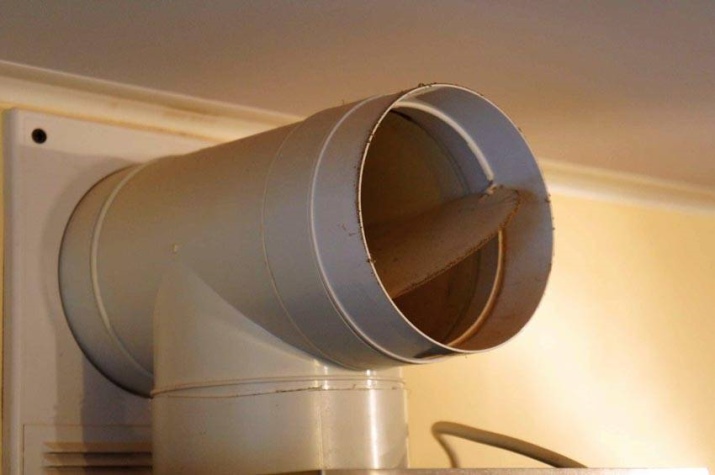

Replacing the hood with an ordinary stove is achieved by installing an ash pan below the level of the floor covering. But this is only possible during active use. If the stove burns briefly, a reinforced ventilation system will be quite relevant.
A metal stove provides ventilation for the foundation, which will help get rid of a chronically musty odor.
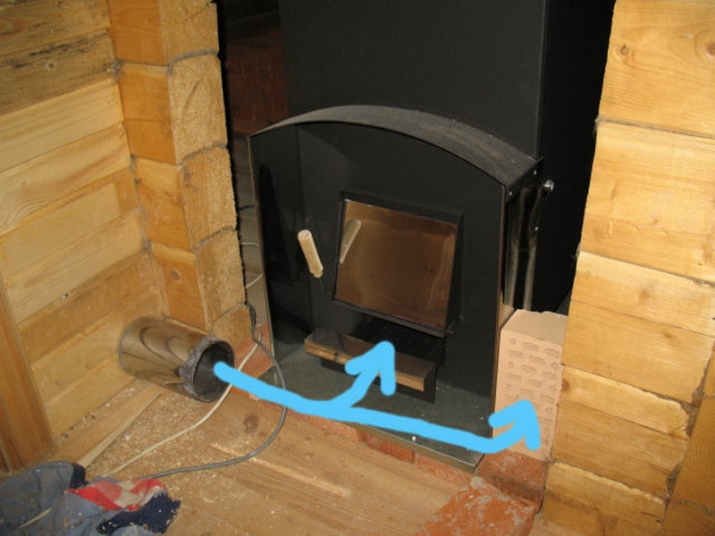

To supply air into the basement and remove it from there, stainless steel pipes with a cross-section of 11.5 cm are usually used. It will pass from 300 to 600 liters of air per minute. This solution is justified if the underground space is single under all rooms. The boards themselves are laid loosely, with a step of 0.5-1 cm; this gives a full gas exchange for ¼ hour. Auxiliary thermoregulation is provided by opening the door to the anteroom.


Bathroom
The circulation in the washroom is often forced; the choice of technical components must be made with care. The exhaust vent must be tens of centimeters larger than the point where the supply is located. It is unacceptable to place the ventilation valve upstairs. Exhaust openings in the washroom must be equipped with shutters, and the floor must be equipped with an exhaust vent. The exhaust must be supplemented with a fan and the pipe that is connected to it must be placed on the roof.


In the anteroom
When designing the ventilation of the pre-bathroom should provide an active withdrawal of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. Exhaust outlets shall be placed a little lower than the ceiling. Supply ducts should be located strictly opposite them. Usually, the intake opening is made closer to the stove to accelerate heating in the cold season, reduce cooling in the winter months. Important: do the pull-out hole directly in the ceiling should not be made, as otherwise the room will cool down excessively quickly; When building a brick bathhouse, all ventilation circuits must be equipped only with forced systems.



In the recreation room
A competent step-by-step guide cannot avoid the topic of air exchange in this room as well. It follows approximately the same principles as everywhere else. If the space is small (and it usually is), periodic ventilation through the door is enough. But if a large room is equipped for leisure, you need a combined system. According to professionals, it is better to make it not with the connection to the furnace, but with small ventilators.


There are many other subtleties and nuances, which is important to consider. For example, the ventilation of the bath has its own features through the floor. Under it, directly in the foundation, holes are made. Holes for the inflow of air are formed in mutually parallel walls. Note: it is impossible to leave the channels open, so that insects and rodents do not penetrate through them; special grids will provide the necessary protection.
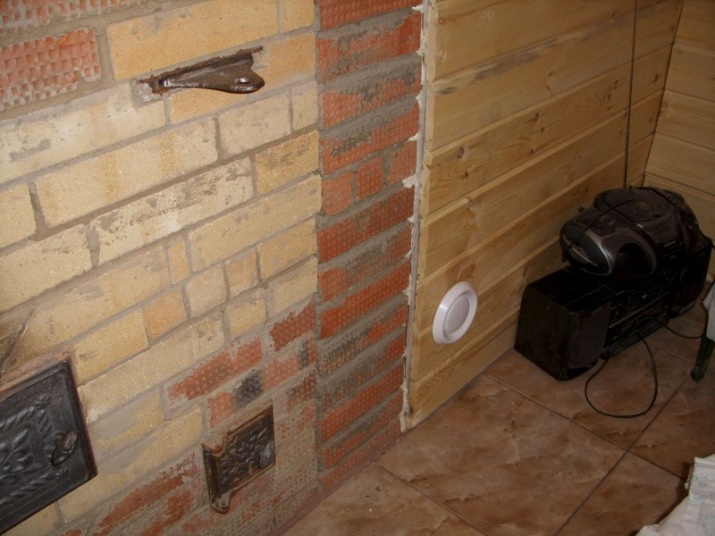

It is worth noting that a simple and comfortable way to ventilate floors in baths is to place it a little higher than the stove's ash drawer. Or, the same thing, placing the stove in the lowering. When installing the valves under the battens, you can only work in the "open" or "shut off" positions. Adjustment is simply not practical. The radius of the first outlet device should be larger than that of the second, otherwise normal operation is not possible.
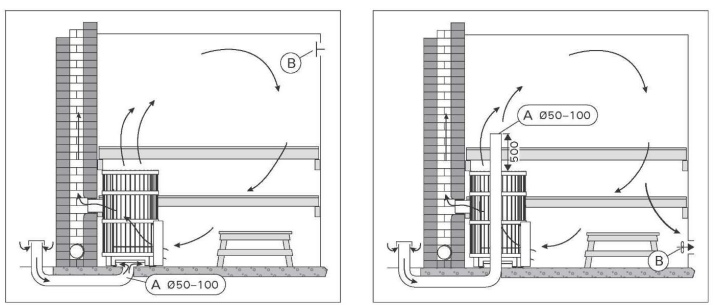
Blowouts in the foundation play an important role. You can talk for a long time about the advantages of simple or complex systems in the installation and use, but if there is no ventilation of the underground space, nothing will work. It is worth considering that the geometry of holes has almost no effect on the efficiency. Thus, if the masonry foundation is formed of cinder blocks, you can use rectangular ducts; in terms of performance, the round design is the best. Outlets need to be closed with caps.

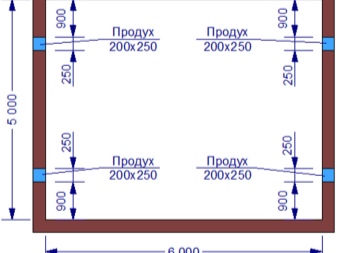
To make the vents look more beautiful, they should be made on the basis of special plinth deflectors. They use decorative grids. In the norm, the foundation windows are required to be placed in increments of 2 m. On plinths without partitions, it is necessary to place the vents symmetrically on the opposite walls. If there is a partition, the ventilation ducts should be located on the 3 parts of the basement that are in contact with the street, and additional ducts should be located directly on the partition.
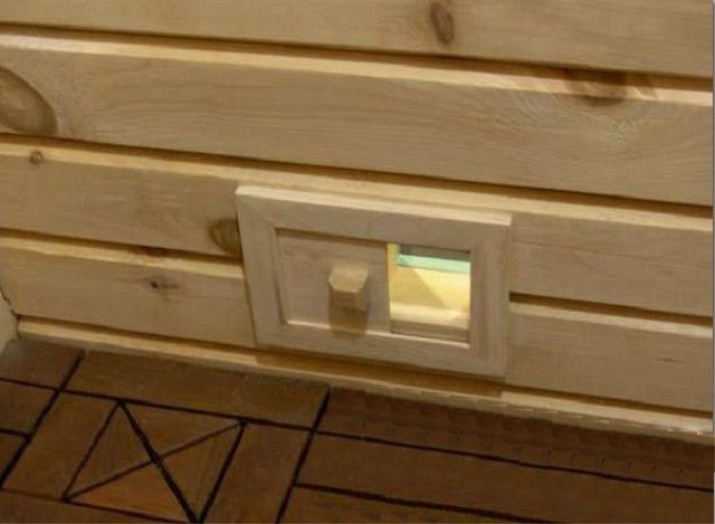

The vents can be installed directly during the construction phase. When installing the formwork under the strip foundation, holes are punched in the sides of the panels. The cavities are filled with sand to prevent the plastic from being crushed by heavy concrete. The pipes are supposed to be placed on top of the armature. When the mortar sets, the sand is removed immediately.
In the case of precast foundations, you can cut holes with diamond drill bits. In bricks they are sometimes punched with long chisels. As an alternative, drills or demolition hammers are used. But it should be understood that powerful blows can disrupt the quality of the tape. During the pouring process, instead of pipe fragments, you can use foam assemblies.


In a classic Russian bath, the ventilation complex can include a gap for the entire thickness of the wall pie. On the side of the steam room form a decorative window. Alternative solution:
-
A window near the shelf 30x30 cm on the frame (with an opening of 20x20);
-
an air vent in the upper part of the wreath 15x15 cm;
-
15x15 cm under the mullion.


The spatial orientation of the bath has a direct impact on the arrangement of ventilation ducts. Inflow should be located on the side with the highest wind pressure. The exit is placed, quite logically, opposite. To exit freely, it is necessary to avoid obstacles from ridge and slope of the roof, from other structures and parts of buildings. Optimal dimensions of outlets 300-400 square millimeters.
Do not chase too fast air exchange. It is necessary to connect the fans only in accordance with the requirements of modern PUE. Air vents in the basement should be at least 11 cm in cross-section. If it is used not electric, and wood or gas heating, it is necessary to increase the size of all outlets and cross sections of pipes at least 10-15%. This eliminates many problems.





