All about the Roman baths

"In a healthy body a healthy spirit" - said Decimus Junius Juvenal about the baths, and since then this phrase has not been forgotten by mankind in a single century. Nowadays, bathhouses are a familiar phenomenon to everyone, the main idea of which is to take water procedures. Bathing in swimming pools, staying in rooms filled with hot steam in order to improve your health and achieve harmony with your body, are certainly useful ways to spend leisure time. Let's see how such traditions have gained popularity.




How were they arranged in ancient times?
Baths became popular in all walks of life incredibly quickly, because people very soon appreciated architectural complexes filled not only with hot water, but also many other tempting suggestions for spending time.


In ancient Rome, a bathhouse was called a therma. Such complexes could be maintained both privately and in the public domain. It was the public thermae that earned fame because they were significant in terms of the size of the area, the scale of decorations and the variety of services provided.
The Roman Baths are often called monuments of world importance. They are admired for the genius of their architecture. Even in our age it seems difficult to do it again.



Until now, it has not yet succeeded, and many people wonder what the secret of the structures is.
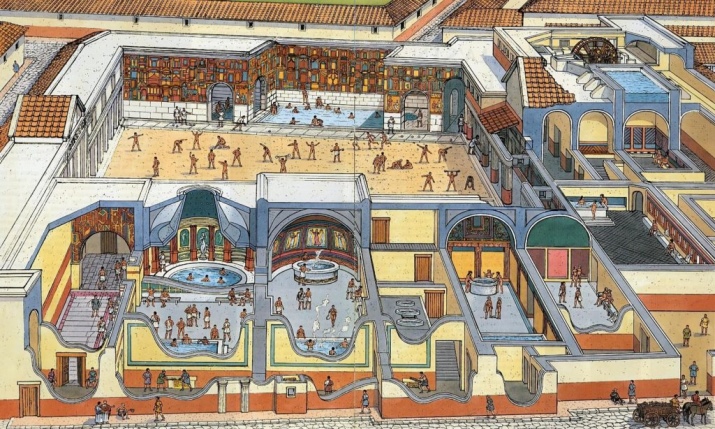
Even earlier thermae existed in Egypt, in Ancient Greece. But it is the ancient Roman model that is remembered. It was a large building complex, divided into sectors by two corridors. Immediately after the entrance to the huge terme, there was an area called the apoditerium: a room in which those who entered took off their clothes. The clothes and other things that people left here lay and waited on specially equipped shelves and niches for their owners until they had finished their procedures and ablutions in the rooms following the apoditerium.


These zones, in which the Romans moved successively from one to the other, are something of a cycle, an outlined plan for a smooth progression on the road to purification and relaxation. The tepidarium contrasted in temperature with the previous locker room. Here the temperature was slightly higher than at the entrance, rising about 10°, and the humidity was moderate.


In the calidarium it was very humid and hot. There, along the walls or in the center of the room, were baths which called forth their vapors and fragrances. The laconium was designed to be steamed up at the highest temperatures, which reached 80 degrees Celsius. In this area it could not be humid: dry steam (humidity of 15-20%) swirled in the walls of the laconium.

After a man enjoyed the hot baths, he prepared to complete his water procedures in the Roman bath in contrasting warm temperatures. But he still had some other rooms to go through. From the laconium followed to the frigidarium: a steam room that contained two pools. One contained warm water, the other cold water. The contrast bathing was beginning.
Finally, the last bath for the Romans was the natatio area, represented by a large pool of water, the temperature of which was neither warm nor cold.
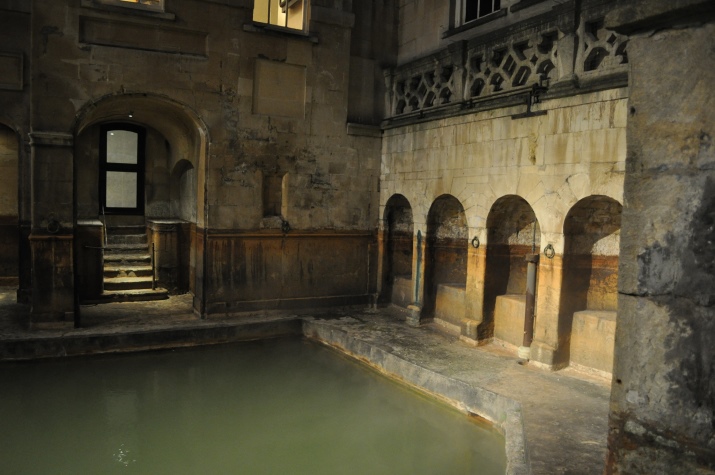

It must be said that all the rooms of the baths in ancient Rome were spacious, and in total one complex could occupy an area of up to 100,000 square meters. The Roman baths were always crowded and noisy. In addition to a few thousand bathers, thousands of slaves (balneators) worked tirelessly in the baths.
They kept the hypocaust, that is, the heating system, in constant operation. The furnaces were heated with oil and wood, and no smoke was allowed. The baths of the Roman type were characterized by the principle of bathing in hot air and warm water, which the thermae quite allowed.


There were pipes in the thermae through which air heated by furnaces and from boiling heated boilers entered the space inside the walls. The steam increased the humidity in the tepidarium and the calidarium. Thanks to a carefully calculated and worked out to the smallest detail system of the hypocaust, conditions were maintained in all the rooms. Hearths heated the air in the laconium, but the surfaces in Roman thermae, despite the constant fire, were not scorched: the floor, like the walls, was double and had cavities heated by the furnace from below.
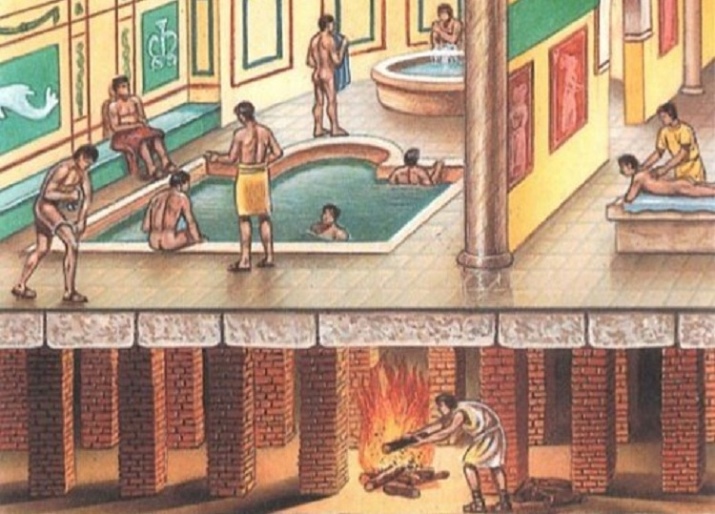

The water in the warm pools was medicinal, because the baths were built near hot springs. At that time, the territory of the Roman Empire abounded in resources of water of this type.
Therefore, thermae, firstly, used for their baths only ecologically pure and saturated with useful natural minerals water, and secondly, had the ability not to be stingy and use as much water as needed to change the water in the pools twice a day for the next group of three thousand visitors.
A prerequisite for good Roman thermae was a rich decoration of the premises. Marble walls painted with drawings and decorated with precious stones, golden statues, high dome ceilings, mosaics and columns with intricate and exquisite ornaments are by no means a complete list of the interior decorations of these bathing rooms in ancient Rome.
To the main areas for bathing and fun adjoined rooms where real theatrical performances were staged, athletic competitions and games were held, and admirable feasts were also held.
Modern versions
Ancient Roman thermae are the model for all modern baths. The Greek tradition of ablutions in the baths that came to Rome spread all over the world. Do not forget that the Roman Empire was one of the strongest powers, which conquered territories and conquered people, spreading its culture to other states in Europe and Asia. The culture of Rome is inconceivable without its thermae.
Ancient Roman emperors built thermae everywhere. This is how they got to us. Even today, it is possible to experience their fabulous atmosphere. This can be done on a grand scale in large spas, fitness centers, hotels, resorts in Italy (popular thermal springs in Montecatini, Abano-Terme).
Roman thermae in their homeland are quite well equipped.




Such baths consist of a steam room, frigidarium-type rooms and additional places for various health and beauty treatments. For example, in every Roman bath there are rooms for massage, chromotherapy, etc. Elite and at least reputation-conscious salons try to make their baths worthy successors of the ancient Roman baths, so they try to create therms, which resemble their "ancestors" by the microclimate conditions and interior design.




The steam room is an analogue of the Callidarium. It is equipped with seats and beds. The temperature in this room is 40-60°C and the humidity is 100%. A modern frigidarium is a room with two pools. In one, the water will be cold, in the other - hot. The ancient Roman style of decoration - mosaics, frescoes and other exquisite decorative elements. All this tries to recreate today. Panels, fountains, marble can also be found in modern thermae in Rome. Modern thermae are built on a somewhat smaller scale. Saunas and baths with jacuzzis can be small in size so that only a few people or even one person can use them.




The most common type of sauna is one with a working stove, wood or electric. It is best to have an electric sauna inside your own home because it is safe and easy to use.
If a wood stove is chosen for the sauna, it requires constant monitoring of the work, the stability of the heat and humidity indicators. In the sauna the temperature is maintained at 60-100 ° C, the humidity is 10-13%.
After steaming in such conditions, one usually moves to a cooler room. The newest invention is saunas with infrared heating. The temperature inside such a cabin is about 60 degrees, the air is not too hot, the heat is radiated by the walls panels of Jacuzzi (countercurrent) - it is a massage and relaxation of the body by streams of water, stimulating the activation of metabolism.



How do you take a steam bath?
The thermae in ancient Rome were a great place to have fun, and most importantly - useful. All conditions were created for this: a disposing environment, pleasant company, and many recreational activities. Roman baths were surrounded by gardens with green vegetation, and the healing properties of thermal waters contributed to the rejuvenation of not only the soul, but also the body. Bathing in such pools purified and toned the skin, had a beneficial effect on the organs, muscles and nervous system.
Even now, visiting the baths is highly recommended by doctors and beauticians: it is noticed that those who have the habit of regularly going to them, have a strong immune system, are less likely to catch colds and respiratory infections.




But it is necessary to sweat properly, this is the only way to achieve the desired effect.
- If you have any disease, which at the moment proceeds acutely, then refrain from going to the bath until recovery, consult your doctor.
- Sauna with infrared radiation can be harmful, because the rays that artificially affect the human body, do not clean the body, but subject it to stress: in nature, these same harmful rays are completely absorbed by the atmosphere before reaching the surface of the Earth.
- Before you go for a steam bath, properly stretch: stretch, do lunges, bends.
- Use olive, castor, sesame or almond oils when washing. Oils clean the skin better than soap.
- Use a brush with natural hair.
- Go into the steam room no more than three times, each session lasting up to 15 minutes.
- Young children can be harmed by a long stay in the baths and thermae. For them it is worth reducing the number of times and approaches.



As the Roman baths looked like, see below.




