All about the waterproofing of the bath

The modern bathhouse is not limited to wooden construction, many people give preference to strong and durable structures made of brick or aerated concrete. However, even the toughest materials in contact with moisture and frequent changes in temperature (outside and inside) are prone to fungus and mold, which reduces the service life and a healthy indoor climate.


Requirements
The main requirements for selecting quality raw materials are:
- waterproofness and vapor permeability;
- resistance to aggressive media, mechanical stress and bacterial growth;
- weather resistance and durability at severe temperature fluctuations.


Materials
Correct work on waterproofing is necessary in every project, which is especially relevant to the Russian climate in general and to the construction of baths in particular. Such work applies to all architectural elements - from the foundations and walls, to the ceiling and roof, so both the primary and secondary overhaul is possible. It is not difficult to do due to modern technologies and innovative materials.
Waterproofing can be external or internal. The choice of one or another method of protection depends on many factors such as time of year, budget, materials of the room (foam blocks, bricks, wood, aerated concrete blocks), so you should familiarize yourself with each of them in advance.


Let's list the main materials for protection against water penetration from the inside or outside.
- Mastics of different composition (one- and two-component) For coating in several layers inside and outside. Depending on operating conditions, the thickness varies from a few millimeters to a couple of centimeters.
- Roll-fed coating made of flexible materialsThe most common material for vapour barriers is a roll covering, which is glued to a flat surface (not suitable for geometrically complicated project details). For vapor barriers, the most common material is foil on a woven and non-woven base.
- Paints and varnishes with various resins, polymers and silicones to apply 2-4 layers with a thickness of about 0.5 mm. The main condition is deep penetration into the porous substrate, but may require protection against sliding and reinforcement between layers.
- Liquid rubber (or PPU spraying), which both insulates and insulates, but it is difficult to install and requires special equipment and knowledge.
- Colmatizing compounds (antihydron) for impregnation of concrete and brick surfaces, which are first thoroughly cleaned. There are also special impregnations for wood, but their class of reliability does not apply to waterproofing. The advantage is the repairability and durability of the result.
- Injection polymers (such as "Gekkon") For the most problematic places, cracks and holes. Requires calling a specialized team with tools to create high pressure.
- Superdiffusion membranes To cover flat surfaces that are permeable to steam. Requires not only expensive professional installation, but also themselves are quite elite and difficult materials.




Various types of plasters and paints, polymers, PPU, rubber, roofing felt, membranes, modified bitumen and foil are used both during the construction phase and in the subsequent repair of the bath. Waterproofing of the walls under the tiles or under the wood, ceiling, exterior facade and roofing, steam room and washroom, floor slabs, and including the foundation, to protect against groundwater.


Important! Many manufacturers indicate quite low allowable temperatures when working with materials, but experienced installers do not trust any information on the labels and follow their own observations in practice.
Separately, it is necessary to emphasize the importance of not only the passive, listed above, but also the active waterproofing of the bath, which ensures its durability by 70%:
- good ventilation;
- uninterrupted water drainage;
- high quality under-floor construction;
- a set of measures to ameliorate the agroclimatic conditions of the site for construction.


Methods of application.
Protection of building structures depends primarily on the selected materials. And there are only 2 options for applying waterproofing - either coating or pasting technique. The first option is the most common and budgetary and is convenient in every hard-to-reach corner. Some materials can be simultaneously plastered on the walls and foundation in several layers (the number and thickness depends on the building) to level out and thus obtain a continuous even and seamless coating. Repainting is possible.
Veneer is more durable and difficult to install, so it requires more knowledge of the technique of execution and experience in their implementation, often not available without the use of specialized tools.


How to do?
At temperatures above 100°C, polymers begin to melt, despite claims by manufacturers of foil rolls that the upper threshold of 140°C is acceptable. Therefore, the combined use of several materials is the best solution. For example, to put fiberglass with foil on the ceiling in the steam room (which is especially relevant for wooden ceilings) is better in combination with clay or concrete.
Instructions:
- The wooden base is lined with roll material for baths and saunas (isolon, tepofor, foam-therm);
- a layer of up to 3 cm of cement mass with dry sawdust or straw is spread on top;
- then a composition of liquid clay and vermiculite is applied;
- left to dry for 14-60 days, depending on the time of year (in winter, respectively, longer than in summer);
- laying polymer insulation (polyurethane foam, mineral wool);
- is applied foam crumb in the cement mortar.



Aluminum in foil allows not only to protect the supporting structures from moisture, but also to maintain a comfortable temperature and accelerate the process of heating the bath. At the same time, it is very important that the layers are made without joints with aluminum tape.
Foundation
High-quality waterproofing of the foundation is made with a pillow (about 20 cm thick) of drainage materials such as sand and gravel. This is necessary to avoid stagnant fluid under the bath. Then a framework is made of formwork, where the concrete is poured until it hardens completely. Only then proceed to the main work on waterproofing. For them it is necessary to glue horizontally 3 to 5 layers of rolls of ruberoid or optionally take any other material such as bituminous-polymer mastic.
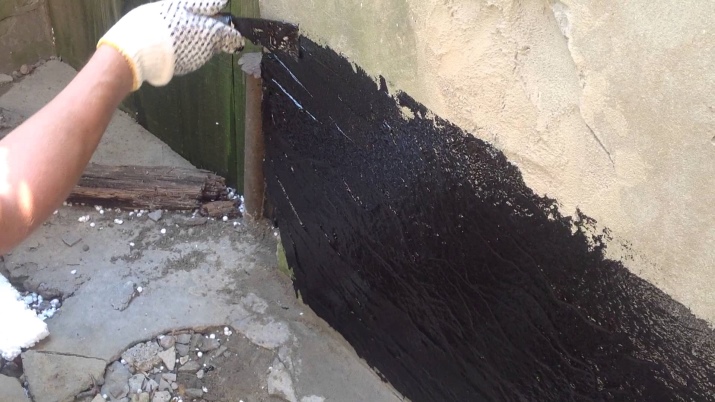

On the walls, too, waterproofing is glued or smeared (depending on operating conditions and budget), and docked with horizontal rolls at the bottom of the foundation to prevent leaks.
The second method of waterproofing the foundation is plaster (up to 2.5 cm thick) of mineral cement with increased moisture resistance. After that, the foundation pit is filled with greasy clay for additional insurance against groundwater and flooding.
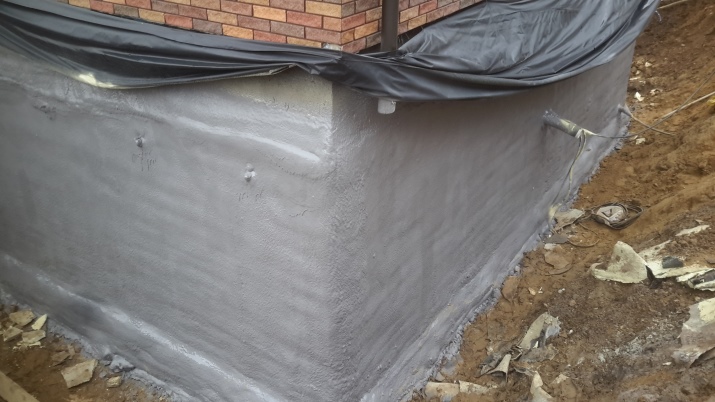

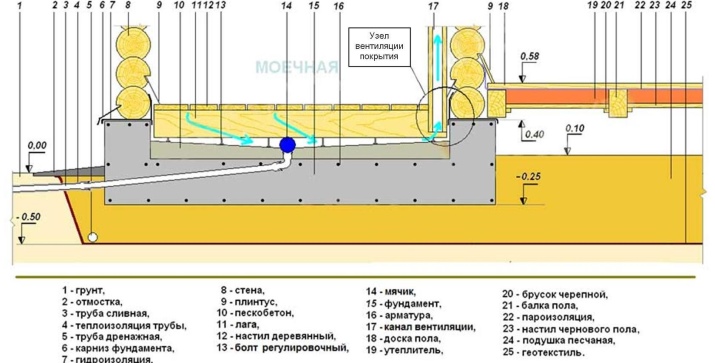
Floor
Even the coniferous floor (which is considered sufficiently moisture-resistant, unlike the coating of other types of wood) in the steam room and washroom will eventually rot, so in the construction of the floor for baths and saunas give preference to concrete. You can choose a roll material on the type of waterproofing, which is laid with an overlap on the wall, and the joints are foiled with aluminum tape, then put the reinforcement and concrete again. After that, you can lay tile or wall cladding.
First waterproof the walls, and then you can proceed to the flooring.
As protection against moisture liquid glass is used in combination with mastic or plaster (which works simultaneously as a screed) and other mixtures.

Before this, it is specially aligned by the water level, observing a 10-degree slope to the center, where the drain is located. Wastewater goes into a pre-equipped sewage system. If rain and groundwater cannot drain properly, it will infiltrate the foundation. If the water is not directed out of the house by the drainage system, it will accumulate around the foundation, where it will try to find its way in.
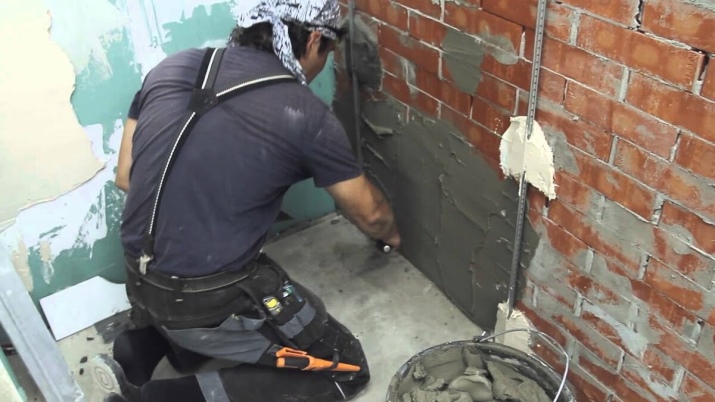
Walls
Plastering the walls with a waterproofing mixture in 3-5 layers is very popular due to the low price of materials and the relative ease of installation. In addition, this option is the most economical when laying tiles in the washroom. The outer wall is lined with roll materials with foil, and a gap must remain between the facade sheathing and waterproofing.
In addition to combating mold, it gives additional protection against heat loss. The joints are treated and caulked, the edges of the sheets should be longer than the wall at least 30 cm to avoid leaks. Then you are going to nail the linings on top of the foil.
When the facade is exposed to precipitation, they can get inside the walls and in some cases pass through to the interior coatings. Waterproofing exterior brick walls helps solve moisture problems. This can happen due to cracks, so insulating with special plasters will solve the problem.

Roof
In any construction, when it comes to the durability of a building, check the level of waterproofing of the roof. It should be borne in mind that the roof occupies 30% of the surface of the structure, so it is necessary to properly implement its waterproofing. To ensure that the rest of it is protected from damage due to water seepage, it is better to choose a pitched design, as flat ones require special protection. If the new roof will be waterproofed correctly, it will increase the life of the structure, which will be very convenient for residents, as well as increase the reputation of the builder.


Effective waterproofing and vapor barrier is the most important part of the roof, this is true for the steam room and other wet areas.
For example, a low-permeability waterproofing membrane on the roof to vent excess steam is especially useful in frequently heated saunas. However, the requirements for weather conditions are an important aspect, which is often limited to contractors, especially in the spring and fall in the Russian climate.
Liquid polymer membrane is a thin coating, which usually consists of 3 layers: a primer on the bottom and 2 polymer on top. The liquid hardens and turns into a rubber coating with a pulling action of up to 280%. They are applied by spraying, roller or trowel. This material gives more flexibility and reliability to the structure than cement. Durability depends on the type of polymer the manufacturer uses.

The problem of waterproofing a bath must be handled with extreme care, and care must be taken to ensure that the materials are used correctly. Waterproof coatings can resist temperature fluctuations and close off microcracks, preventing water ingress.
For more on waterproofing in a bathhouse, see below.




