What is a bath and what is it?

Many people do not know too well what it is - a bathhouse, what are the variants of bathhouses. And yet their history and description is quite remarkable and instructive. It is equally important to pay attention to what a bathhouse consists of.






What is it?
If you turn to dictionary and encyclopedic sources, they clearly indicate that the word bath has its roots in the Latin language of the ancient Roman period. Depending on the particular type, the combination of water and hot air or water and steam affects the people washed there.



Different regions have their own traditions of bathing procedures, which depend on natural conditions and a number of other factors. Everywhere around the baths was built traditionally specific etiquette and approach to hygienic procedures. Nevertheless, everywhere this or that building where water is heated and used for bathing.



History of appearance
The most famous are the ancient Roman "thermae", which worked thanks to a sophisticated infrastructure. However, other leading civilizations of antiquity also had baths. At that time, there was already a clear structure of rooms, each with its own specific function. The importance of Roman thermae is considered greater than in other cultures because they were also one of the centers of cultural, social life.



In the Middle Ages, there were no longer such huge complexes. - but contrary to popular belief, not so much because of Christian restrictions as because of the decline of material culture. Only a certain number of the old baths were still in operation. New public baths began to appear in the ninth and tenth centuries, when the effects of decadence had largely been overcome.


Paradoxically, but it is a fact: in the sixteenth century, against the background of the growth of material culture as a whole, European baths were in decline.
Wood was actively consumed as fuel for metallurgy and raw materials for building ships, and heating became more difficult in the conditions of a small ice age. In Islamic countries, bathing existed more or less steadily, not experiencing sharp ups and downs.


On the territory of the modern CIS the bathhouses were also quite popular.The bathhouses were also quite popular in the modern CIS, although without the fantastic superiority over other countries that is often written about by authors with little knowledge of the subject. What is certain is that the type of bathing itself was fundamentally different.



Over the course of time, baths everywhere evolved. Their appearance changed dramatically in the nineteenth and especially in the twentieth century due to the emergence of new modern materials and means of heating. But, as many centuries ago, the baths still achieve the same goals and allocate all the same basic parts.



What does it consist of?
It depends on the financial capabilities of the owners and on how much space is available. If it is possible to allocate a large area for construction, then the steam room will be clearly separated from the washing room. Otherwise they have to combine. The steam area is usually equipped with shelves of different heights.



Additionally can be allocated:
- anteroom;
- rest room;
- room for temporary accommodation;
- boiler room.
Description of types
There is a great variety of types of baths, each of which has certain differences.


Russian
Although there are many other types of baths, it still makes sense to start with the most familiar and corresponding to domestic traditions. Obligatorily used in this version of the stones, when pouring water over which there is hot steam. Another typical feature is the use of birch leaf brooms. In addition to the purely hygienic purpose of the Russian bath has a very powerful health-improving function.
But it is important to understand that such an intensive influence on the body may not be too useful, and therefore caution should be exercised.



Finnish Sauna
Scandinavian "buddy" of the Russian bath is both similar to it, and at the same time different. This difference is so significant that no connoisseur would confuse these options. The most important feature is a very strong heating of the air. No one is surprised by the temperature of 130 degrees.


In various "competitions" sauna visitors are at a temperature of up to 200 degrees. It is logical that you can carry such a heat only in very dry air (with humidity not more than 15%, and ideally not more than 10%).



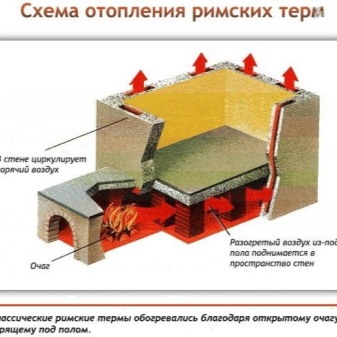
Roman
If Russian and Scandinavian baths are mainly finished with wood, then the Roman variety means facing with marble or granite. Temperature there is much lower: from 45 to 65 degrees, depending on the zone.
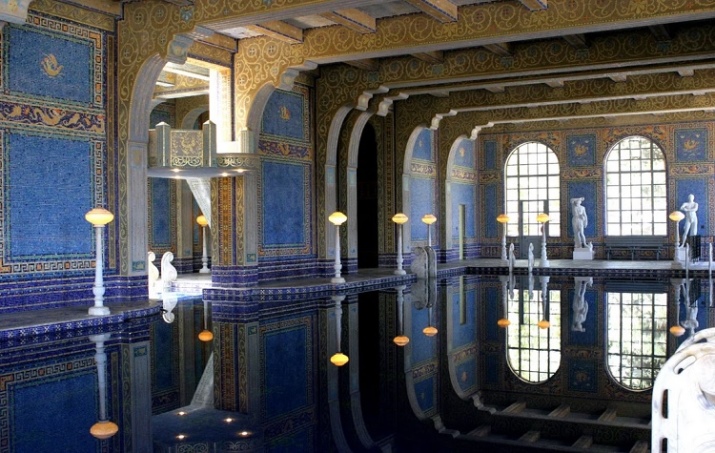

The main effect is not so much due to heating as to humidification. Experts note that the therma has an excellent cosmetic effect. Rooms are equipped with benches of varying height, and a fountain is sure to be used.

Turkish
While both Russian and Finnish baths belong to the steam type, the hammam has unique features, although it is just as much an adaptation of the modern Roman "caldarium". A characteristic feature of the Islamic bath is the presence of the chebek, which is a round stone that is always kept warm.
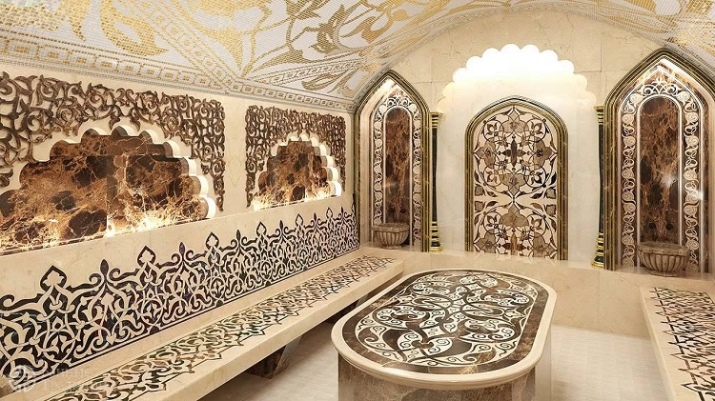

Also the Turkish approach implies the use of kurnas, that is special vessels with water. Humidity should be only 80%. The temperature usually ranges from 50 to 55 degrees, according to the traditional religious canons hammams are divided into men and women.



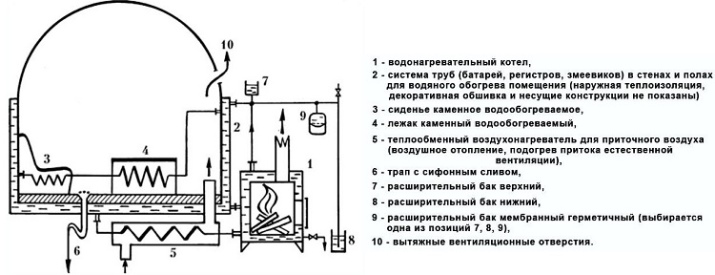
Irish
In its development, this version of the baths still starts from the antique prototype. Similarity can be already seen in the organization of heating. The heating is provided traditionally by round or square vaulted stove. The construction was designed in such a way that the floor covered with brick slabs and faced with marble would heat up slowly. Such a bathhouse would also take quite a long time to cool down.

The Irish approach involves directing hot air under the floor. From there it moves along the walls through special pipes. The coldest part of the Irish bath is designed for a temperature of 25-27 degrees. The other two segments contain air heated to 32-35 and 50-60 degrees, respectively.
Even in the hottest room it is easy and pleasant to breathe, as the inflow of fresh outside air through a separate pipe is necessarily supported.
Japanese
We need to make two marks here. Firstly, the Japanese bath developed autonomously from the European approach. Secondly, it is even visually a very special phenomenon.

Traditionally, the inhabitants of the Land of the Rising Sun valued a decent flow of fresh air. There is no division into the steam room and the washing room. Both are replaced by a large wooden tank, and you can rest after bathing on a special couch.



The reason for such an original structure is obvious: Japanese bathing follows a very special philosophy characteristic of this Asian country. The use of soap has been forbidden there since ancient times. It was only possible to compensate for this Buddhist prohibition by using strongly heated water.
In addition, the limited amount of wood in Japan forced the construction of thin walls, and only a barrel of water allowed to insure against hypothermia and drafts.
Another unique motif is that the barrel simulated bathing in a thermal spring, of which there are quite a few, and yet they are not everywhere.


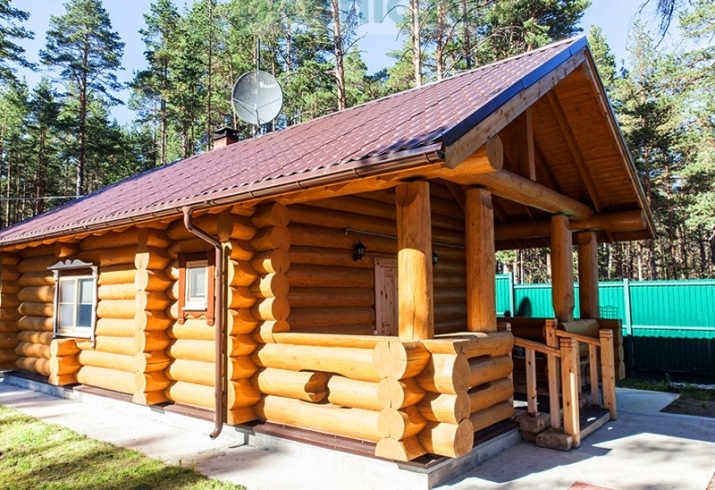
Projects
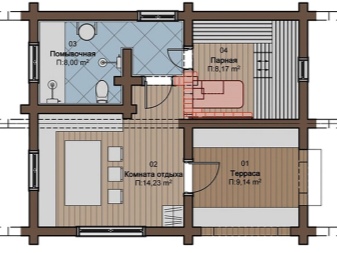
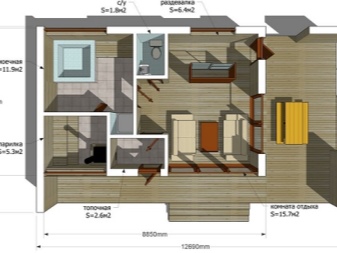
Schemes of baths can vary significantly. Quite a decent option involves equipping a 6-meter shower room. The area of the steam room will be 1.5 square meters less. But there is space for leisure on 8,8 m2. The designers of the scheme took care of even a relatively small porch.
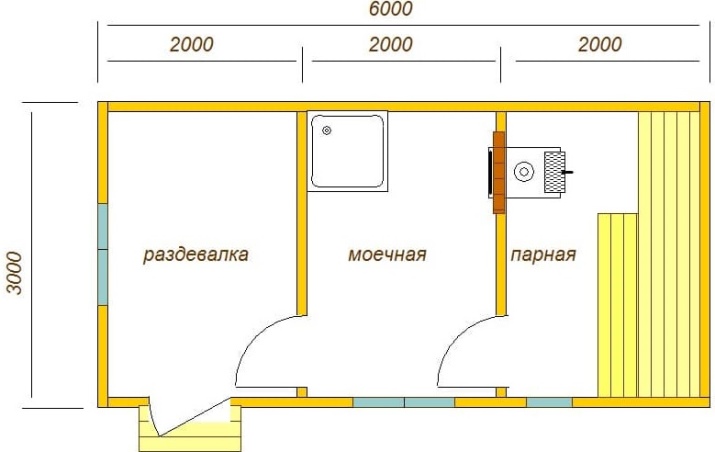
You can use a different approach. There are two porches, one of which leads to the terrace and the other to the recreation room. Additionally provided:
- a washroom;
- a steam room;
- a vestibule;
- a comparatively small bathroom.
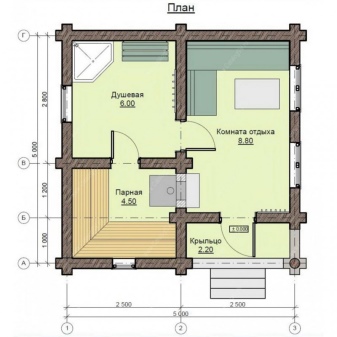
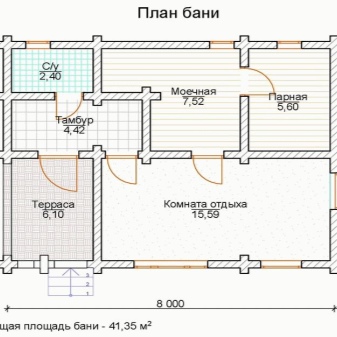
How to build?
It depends, first of all, on the chosen type of the bath. However, it makes little sense to consider Japanese, Irish and other options. In at least 95% of cases a Russian bathhouse or sauna is built - these are the formats that you should consider in the first place.



Russian bathhouses usually have dimensions of 2.5 x 4 or 3 x 5 m. The building is erected on a pillar foundation of shallow type. Log house is often made of selected wild logs, without the use of nails. The gaps between the logs are filled with oakum and moss. The ceiling is made flooring type. A combination of moss and peat is used to insulate the floor and upstairs.
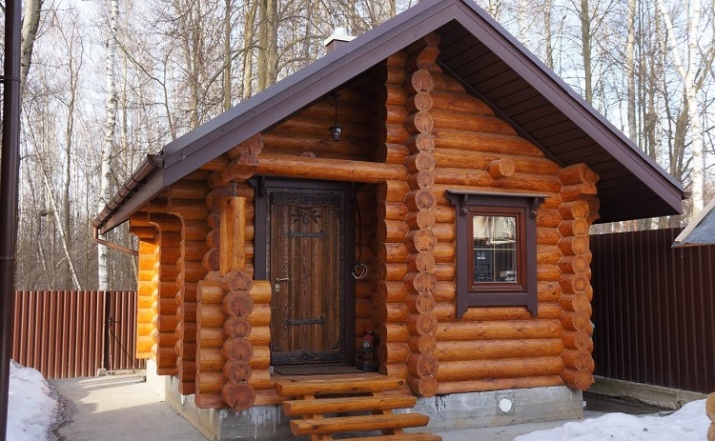






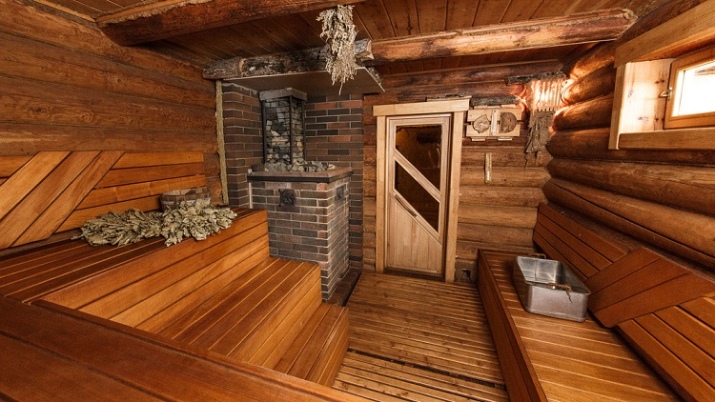
Protection against the penetration of moisture is provided with the help of resin and cobbler, and the roof is carried out on the turf or shingle method. Also any Russian bathhouse in the true sense of the word is equipped with a brick stove.



To replace it with other heating devices is not recommended. Important: the area of the room and the size of individual zones chosen at your discretion, and they must be calculated very carefully. For 1 permanent visitor should be at least 1.8 square meters of the anteroom and 1.5 square meters of the steam room. The ceiling height 240 - 250 cm is enough to bathe in the bathhouse people of all sizes.






It is worth considering that the construction of a good level bath is incompatible with austerity. Only first-class coniferous timber is good for it. Logs are much inferior to logs, but the logs themselves will have to be chosen very carefully.

All lumber should be bought by carefully measuring with a tape measure and inspecting all sides to detect even small defects immediately. If the bath is built on a strip foundation, then you can not spare the concrete, and the concrete must be of first-class quality, it is also very useful to strengthen the base of a reliable armature.



All wooden elements of the baths should be impregnated with compositions protecting against fire and biological threats. Despite this, near the stoves, around the chimneys and in other similar places should be respected fire breaks, asbestos lining is also recommended. Waterproofing materials are additionally treated with bitumen mastics.
In the arrangement of the foundation and the floor should not forget about maintaining a certain slope.



The stone floor is improved by a wooden crate. The rafters should be covered with roll waterproofing and wooden flooring. When creating the ceiling boards are laid with a step of 2,5 m. Inside the Russian bathhouse is mainly finished with clapboard. For exterior decoration can be used:
- vinyl or steel siding;
- cladding made of plastic;
- Block-house, which reproduces the look of a log cabin;
- edged or unedged board.
Construction of the sauna is easiest to conduct a frame method. This construction has another important advantage: it heats quickly and does not require much fuel or energy. The size of the construction is determined in exactly the same way as in the case of the Russian bath. Looseness of the soil or location of the site on a slope, usually forces the use of foundations on the basis of asbestos-cement pipes. The functionality and beauty of metal pile foundations is undeniable, but it is expensive and creates difficulties in construction.

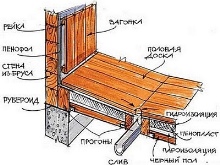

Most people prefer to use a strip reinforced foundation with shallow footing. This solution is not obviously suitable only for saunas located on loose soil. It is worth bearing in mind that both bathhouses and saunas of any type, with any foundation, can only be built with permits.
If the project is not approved, then any complaint from the neighbors is enough for the structure to be demolished, and most likely at the expense of the hapless builders. It is necessary to take into account not only fire and sanitary standards, but also the required power supply (the latter point is especially important when using an electric furnace).


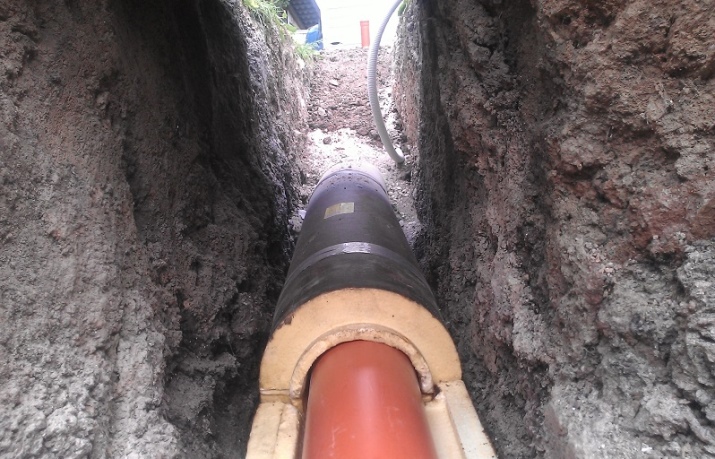
Runoff from the bath or sauna is directed to a separate drainage pit. Feeding it into the general septic tank will lead to its catastrophic overload. Sewage is arranged most often from PVC pipes section of 5 cm. The pipes are laid on a sandy cushion with a layer of 15 cm. The slope of the drainage pipe should be at least 3 cm per 1 pg. m.
Strictly unacceptable undulating laying and placement of the channel above the freezing point of the soil.

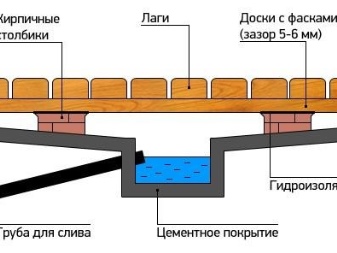
Any water and sewer pipes are specially insulated with a shell of Styrofoam. Only after laying them, you can deal with the foundation. It is advisable not to use homemade concrete, but custom-made concrete. It should stand for exactly 30 days with periodic moistening - only in this way it is guaranteed to gain strength. Particular attention must be paid to the quality of waterproofing and to ensure that it is not violated anywhere.

Insulation of baths and saunas is better to do with the plates based on basalt wool. On both sides of the insulation is laid aluminum foil. The simplest construction usually involves the use of a single-pitch roof. If the size of the bath is limited, you can even put it without the maueralt. Thermal junction for the passage of the chimney and pipe, as well as their junction should be thought out in advance!


How to arrange?
But no matter how good the "box" of the building, the base and the roof, you can not do without it. It is necessary to take care of the finishing. Mostly wood is used for it - but only boards dried to 10% can be used. Ideally, thermal wood should be preferred. The walls of the washing room is lined with pine paneling or tiled.
The floor is most often formed on the planks. On them laid boards made of hardwood. Final finishing is usually performed with tile with a matte or grooved surface. If there is sufficient funding, you can use for the finishing of luxury oak abasi. But most people prefer cedar or even more affordable species - alder, linden and aspen.



The stove is chosen primarily by power. But too strong heating is impractical in the Russian bath, where the stones should be heated in the first place, but not the air. Not every stone is suitable for the bath. Optimally suited to these tasks are:
- gabbro;
- jadeite;
- quartz (crimson and white);
- basalt;
- porphyrite;
- talcochlorite.
It is recommended to finish the washroom with coniferous wood. But if you do not like this option, then marble and tile will also be good. Another washing room should be equipped with good ventilation.
Due to the limited amount of free space in baths and saunas put only small or built into the surface fixtures. Large windows are not practical to equip.



Interesting Facts
The Russian bath is the most humid of all the options. Staying in the steam room for more than 5 minutes even for physically strong people is not safe. But a short visit to her helps to strengthen the heart and respiratory system. And here in the Japanese approach is characterized by the use of sawdust bath - ofuro. You can immerse yourself in sawdust for 10 minutes. In addition to the hygienic value of furo is characterized by the ability to combat rheumatic manifestations and remove stress.

In Germany in the 18th century, it was popular to visit the baths as a whole family, and even with dogs. And in the ancient Roman period, every new emperor, among other things, had to open a new public thermae as soon as possible. The attitude of doctors to bathing procedures is contradictory: they are recommended as prevention of colds, but inadmissible in the acute period.
Among all countries, the leading position in bathing is occupied by Finland. The 5 million Finns can use about 2 million saunas.


But in our country there are also many enthusiastic people - about 20%, according to surveys, at least once a month visit saunas or baths. In order to get the best health-improving effect, you need to do it no more than 2 times a week.

There are a number of other interesting points:
- In Russia from the XV to the XVIII century public baths were common for men and women, and only a special decree stopped this practice;
- The ideal brooms, according to connoisseurs, are obtained from the birches growing on the bank of a body of water (even better, if the branches are bent directly to the water);
- The ancient Greeks used laurel brooms.


In the following video you will find the basics of proper bathhouse planning.




